Renown Class Battlecruiser (1916)
Machinery
Boilers
Engines
Generators
One 175 kw oil generator and three 200 kw steam generators, with an additional 200 kw steam generator added in 1916 or later.[1]
Armament
Guns
The 4-inch guns had blue-tinted loading lights with adjustable shades that would illuminate the breech for night action. These sorts of lights are visible on other guns in many photos. The triple gun mounts had a single switch to control its three lights, located near the assistant trainer's seat.[2]
Torpedoes
- Two Service Bar 21-in submerged broadside tubes forward depressed 2 degrees and bearing 90.[3]
- Eight above water tubes, four each side in pairs fixed at 90 degrees and with gyro angle pads for adjusting torpedoes were initially envisioned, but apparently not fitted as built.[4]
The submerged tubes could not be fired at speeds over 31 knots, as the bar would bend.[5]
Fire Control
Rangefinders
By March 1920, Renown had the following rangefinder outfit:[6]
- Two 30-ft in "Y" turret and in back of GCT
- Four 15-ft in "A" and "B" turrets, TCT and GCT
- One 12-ft in spotting top
- Two 9-ft on fore bridge (for torpedo control)
- One2m F.T. 29[7] HA RF on control top (fitted 1917)
At the same time, Repulse was similar, but had snuck in one more 30-ft RF:
- Three 30-ft in "A" and "Y" turrets and in back of GCT
- Three 15-ft in "B" turret, TCT and GCT
- One 12-ft in spotting top
- Two 9-ft on fore bridge (for torpedo control)
- One 2m F.T. 29[8] HA RF on control top (fitted 1917)
Phones
Main Battery
Secondary Battery
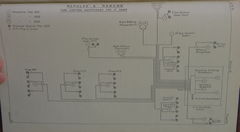

Each 4-in triple mounting had a Pattern 3333 Navyphone for its officer, and a set of Pattern 3225 Telaupad receivers for each of its three sightsetters. The single 4-in guns were similar, but with a single telaupad receiver for the sightsetter. The 4-in TS had a pair of Pattern 3334 Navyphones plugged into its exchange board.[11]
Other remote stations from the TS's exchange board were:
- One Pattern 3331 Navyphone in 15-in GCT
- Two 3334s (apparently teed off from each other in a junction box) in each of
- Forward night defence position
- Aft night defence position
- Spotting top
- One 3331 with telaupad pair in each of
- Forward 4-in director tower (fed from line feeding the spotting top's 3334s)
- Aft 4-in director tower
Evershed Bearing Indicators
The ships contained comprehensive systems for main and secondary battery control.
Main Battery
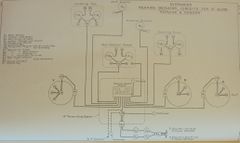
There were four transmitting positions and eight receiving positions. Local COSes at the transmitting positions to select between port and starboard and a selector switch in the 15-in TS controlled the signal routing.[13]
Transmitting positions:
- Spotting top (p&s, with local COS)
- CT (p&s, with local COS)
- GCT (p&s, with local COS)
- "X" turret
Positions 1 & 2 were alternatives to each other and could not be used at same time (a COS in the 4-in TS determined which was in use). Likewise, positions 3 and 4 were mutually exclusive as determined by a second COS. Each position had a junction box of some kind, which may have had a selector switch to choose port or starboard transmitters.[Inference]
Eight receiving positions:
- Turrets "A", "B" and "Y": open faced indicator (for Turret Director Trainer?) and a special indicator (for trainer?)
- Spotting top (indicators suitable for binoculars)
- Light aloft director tower
- Armoured director tower
- Conning tower (indicators suitable for binoculars)
- Gun control tower (indicator suitable for dumaresq)
Secondary Battery

There were eight transmitting positions and nine receiving positions. Changeover switches and a selector switch in the 4-in TS controlled the signal routing.[15]
Transmitting positions, in 4 port and starboard pairs:
- Night defence position forward (p&s)
- Spotting top (p&s)
- Night defence position aft (p&s)
- Manoeuvring platform (p&s)
Positions 1 & 2 were alternatives to each other and could not be used at same time (a COS in the 4-in TS determined which was in use). Likewise, positions 3 and 4 were mutually exclusive as determined by a second COS. Note the difference from the main battery system, where (say) the spotting top's port and starboard transmitters can be used at the same time here whereas only the main battery's transmitter in the spotting top selected at the local COS can be used.
Nine receiving positions with open-faced indicators near the trainers:
- Forward 4-in director
- Aft 4-in director
- Single 4-in gun (port)
- Single 4-in gun (starboard)
- Five separate groups of 4-in guns
Mechanical Aid-to-Spotter
At some point, both were likely equipped with four Mechanical Aid-to-Spotter Mark IIs:
- one on each side of the foretop, driven by flexible shafting from the Evershed rack on the director
- one on each side of the Gun Control Tower employing an electrical F.T.P. system.
As the need for such gear was apparently first identified in early 1916, it seems likely that these installations were effected well after Jutland.[16]
Directors
Both ships were completed with directors for main batteries installed, but the secondary batteries were delayed until each ship was in service for a month (see ship pages for details).[17]
Main Battery


These ships were fitted with 2 cam-type tripod-mounted directors, one in an armoured tower and one in a light aloft tower.[20] There were no directing guns.[21]
The guns could be divided into a forward ('A' & 'B') and aft ('Y') groups. Inferring from other ships with 2 directors,[22] a C.O.S. in the T.S. permitted these control options:
- All guns on aloft director
- All guns on armoured director
- Forward group on aloft director, aft group on armoured director
It is likely that each gun had a local C.O.S. with 3 positions:[Inference]
- Gunlayer's Firing (aux and main circuits connected to local triggers)
- Director 1 (local main to director main, local aux to director aux)
- Director 2 (local main to director aux, local aux to director main)
Secondary Battery

The 4-in guns were supported by a pair of pedestal-mounted directors with double cam grooves and two rollers, one forward (on foremast below the spotting top) and one aft (on mainmast).[24] This placement helped support that subset of the guns capable of firing to either side.
Torpedo Control
Rangefinders
The rangefinder in the TCT was a 9-foot F.T. 24 on an M.Q. 10 mounting.[25][26][27]
Sometime, likely not before 1918, these were to be upgraded to 15-foot instruments, probably also F.T. 24, with new armoured hoods and racers and training driving the hood directly rather than through the rangefinder mounting. These rangefinders lacked hand-following gear to facilitate in transmission of range cuts, and when it was considered as an addition around 1917, space concerns were causing issues. As part of the same initiative, a pair of 9-foot instruments was to be added on each side of the bridge.[28][29]
Transmitting Stations
These ships had a TS for their 15-in guns and another for their 4-in guns.[30]
Dreyer Table
The ships each had a Mark IV* Dreyer Table, probably from completion, and an unknown number of Dreyer Turret Control Tables installed at an unknown time.[31]
Fire Control Instruments

The variety of Marks employed prompts suspicion of the simple descriptions offered of other ships' equipment.
The Annual Report of the Torpedo School, 1915 shows that these ships had quite a loose sense of adherence to Mark numbers in their bill of materials, but included the following:[33]
- Vickers F.T.P. Mark IV range transmitters
- Vickers F.T.P. Mark IV* deflection transmitters
- Vickers F.T.P. Mark III range and deflection receivers (also for repeats)
- Mark III* Barr and Stroud single order transmitter, Mark III receiver
- Mark III Barr and Stroud single range instruments
- Mark I Barr and Stroud fall-of-shot instruments
- Mark III Barr and Stroud combined range, order, deflection instruments
- Mark III* Barr and Stroud rate instruments (some transmitters Mark IV)
- Mark IV Barr and Stroud bearing instruments
- Captain's Bell Pattern 139 and push Pattern 1388
- Buzzer Pattern 1380
- Key Pattern 872
Alterations
In 1916, it was approved that another 200 kw steam dynamo be added to the Revenge, Queen Elizabeth, Renown and (possibly) Furious classes, as the loss of any of the other four sets could impose an undue burden on the remaining generators, especially in a night action. Prior to the addition, the Renown class ships generated 775 kw, or 3,400 amperes.[34]
See Also
Footnotes
- ↑ Annual Report of the Torpedo School, 1916, pp. 120-121.
- ↑ Annual Report of the Torpedo School, 19156, p. 146.
- ↑ Annual Report of the Torpedo School, 1915, p. 36.
- ↑ Annual Report of the Torpedo School, 1916, p. 35.
- ↑ Annual Report of the Torpedo School, 1916, p. 35. (T.O. 145/1916; C.I.O. 1449 of 1917)
- ↑ Burt. British Battleships, pp. 296-7.
- ↑ length and type inferred from reported 6-ft 6-in base length and knowledge of B&S RFs.
- ↑ length and type inferred from reported 6-ft 6-in base length and knowledge of B&S RFs.
- ↑ Annual Report of the Torpedo School, 1915, Plate 122.
- ↑ Annual Report of the Torpedo School, 1916, Plate 68.
- ↑ Annual Report of the Torpedo School, 1915, Plate 122.
- ↑ Annual Report of the Torpedo School, 1916, Plate 71.
- ↑ Annual Report of the Torpedo School, 1916, pp 146-147, Plate 70.
- ↑ Annual Report of the Torpedo School, 1916, Plate 70.
- ↑ Annual Report of the Torpedo School, 1916, pp 146-147, Plate 70.
- ↑ The Technical History and Index: Fire Control in HM Ships, 1919, pp. 25-6.
- ↑ The Technical History and Index: Fire Control in HM Ships, pp. 9-11, 16.
- ↑ The Director Firing Handbook, 1917. Plate 77.
- ↑ The Director Firing Handbook, 1917. Plate 78.
- ↑ The Director Firing Handbook, 1917. p. 142.
- ↑ The Director Firing Handbook, 1917. p. 88.
- ↑ The Director Firing Handbook, 1917. p. 88-9.
- ↑ Annual Report of the Torpedo School, 1916, Plate 69.
- ↑ The Director Firing Handbook, 1917. p. 143
- ↑ Annual Report of the Torpedo School, 1917, p. 198.
- ↑ Annual Report of the Torpedo School, 1918, p. 175.
- ↑ Inferences M.Q. 10 and F.T. 24
- ↑ Annual Report of the Torpedo School, 1917, p. 198. (C.I.O. 481/17)
- ↑ Annual Report of the Torpedo School, 1918, p. 177. (A.L.G. 34150/17)
- ↑ Annual Report of the Torpedo School, 1915, Plate 121.
- ↑ Handbook of Capt. F. C. Dreyer's Fire Control Tables, p. 3.
- ↑ Annual Report of the Torpedo School, 1915, Plate 121.
- ↑ Annual Report of the Torpedo School, 1915, Plate 121.
- ↑ Annual Report of the Torpedo School, 1916, pp. 120-121.
Bibliography
- Template:BibUKARTS1915
- Template:BibUKFireControlInHMShips1919
- Admiralty, Gunnery Branch (1914). Handbook for Fire Control Instruments, 1914. G. 01627/14. C.B. 1030. Copy 1235 at The National Archives. ADM 186/191.
- Template:BibUKDirectorFiringHandbook1917
- Template:BibUKDreyerTableHandbook1918